Survival Strategies of Bed Bugs Explained
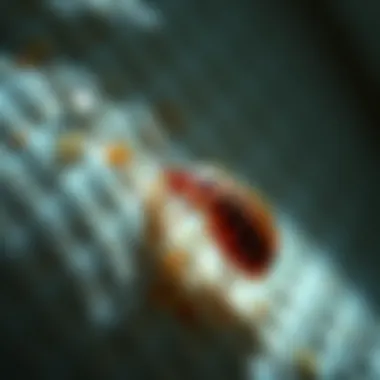
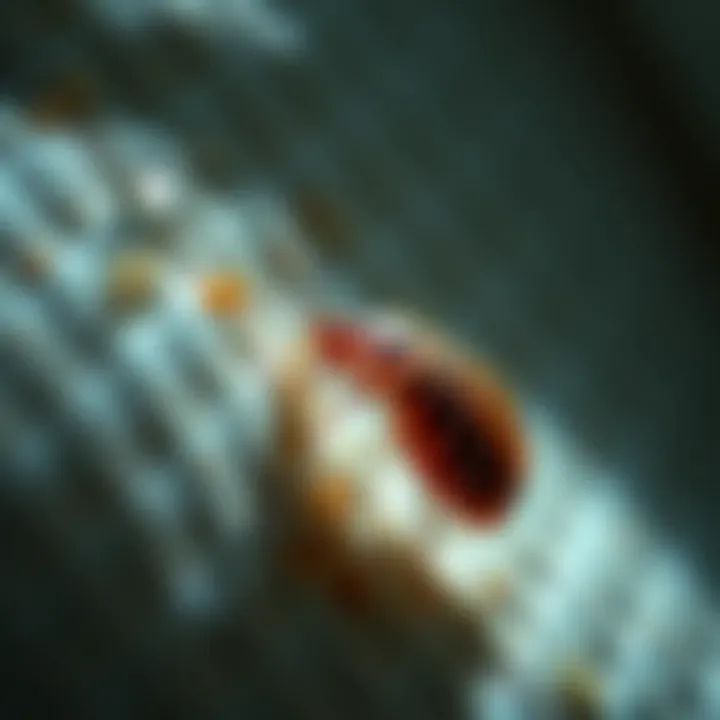
Intro
Bed bugs, though small, wield a significant influence in the lives of many, especially for homeowners and those sensitive to their bite. These pests have intricately developed mechanisms for survival that not only create challenges for eradication but also highlight their extraordinary adaptability. Understanding bed bugs is crucial for successful prevention and management strategies.
They thrive by feeding on human blood, making them expert infiltrators in our most intimate spaces. Their resilience against common pest control methods adds a layer of complexity to their management. By recognizing their behavioral patterns, dietary needs, and ecological roles, individuals can approach eradication efforts more effectively.
This article aims to unravel the survival tactics of bed bugs, providing rich insights and pragmatic methods for dealing with these unwanted visitors. With knowledge comes power, enabling readers—be they homeowners or pest control specialists—to forge a path towards a bug-free existence.
Understanding Pests
Definition of Pests
Pests are organisms that negatively impact human activities, functioning as nuisances or threats to health and property. Bed bugs serve as a prime example of pests that, although not inherently harmful in the conventional sense, can pose significant risks through their bites and the psychological distress they cause.
Importance of Pest Identification
Identifying pests accurately is vital for effective management. Bed bugs, for example, can be mistaken for other insects like flea or carpet beetles, leading to ineffective control measures. By knowing their distinct features, such as size, shape, and the signs of their presence, one can better strategize eradication.
"A stitch in time saves nine" reminds us that early identification can prevent larger infestations and greater trouble down the line.
Prevention Techniques
Home and Garden Preventative Measures
There are various practical approaches to preventing bed bug infestations. These involve not just combating existing bugs but implementing strategies to ward off potential invaders:
- Regular Inspections: Consistently check common areas like bedding, upholstery, and even behind picture frames.
- Sealing Cracks and Crevices: Close off potential hiding spots with caulk to limit areas where bugs can live.
- Using Protective Covers: Encase mattresses and box springs in protective covers, providing a barrier against bed bugs.
- Decluttering: Reducing clutter in homes minimizes potential hiding places for bugs.
Seasonal Prevention Tips
As seasons change, bed bugs often find new opportunities to invade homes:
- Spring Cleaning: Lysol all corners of your home thoroughly during spring cleaning to eliminate any potential bugs or eggs.
- Caution When Traveling: Check hotel rooms and luggage for bed bugs to avoid bringing them back home after a trip.
- Monitor Seasonal Shifts: During cooler months, bed bugs might be more inclined to seek warmth in homes, so increased vigilance is essential.
Eco-Friendly Pest Control Solutions
Overview of Sustainable Practices
Adopting eco-friendly pest control strategies can complement traditional methods, lessening the reliance on harsh chemicals. Techniques such as introducing predator insects and enhancing natural barriers can foster an environment less hospitable to pests.
Natural Remedies and Their Effectiveness
Several natural solutions show promise in combating bed bug infestations. While they may not guarantee total eradication, they can assist in management:
- Essential Oils: Oils like lavender, tea tree, and peppermint can act as natural repellents to deter bed bugs.
- Diatomaceous Earth: This natural substance, when sprinkled in areas of suspected bed bug activity, can help eradicate them by dehydrating them.
- Vinegar Solutions: Vinegar can be used as a cleaning agent to help eliminate bed bug eggs on surfaces.
Utilizing a combination of awareness and practical strategies will empower homeowners and pest control professionals alike to tackle the issue of bed bugs efficiently.
Prelims to Bed Bugs
Understanding bed bugs is essential for anyone wanting to maintain a pest-free home. These tiny, elusive creatures can turn a peaceful dwelling into a battleground if left unchecked. The focus of this article is on their survival mechanisms, which are not only fascinating but also crucial in informing effective eradication strategies.
When it comes to bed bugs, knowledge is power. Recognizing their traits and behaviors can help homeowners identify infestations before they spiral out of control. Without the right information, one may overlook signs of bed bugs until it becomes a more significant problem, leading to sleepless nights and financial strain.
But there’s more at stake. Beyond personal discomfort, the presence of bed bugs poses health risks, as their bites can lead to allergic reactions and secondary infections. For people in urban areas, where bed bugs have found a home in the crevices of public transport and hotels, understanding their ecology and life cycle becomes imperative. This article will provide the insights necessary to thwart these pests and maintain a harmonious living space.
Defining Bed Bugs
Bed bugs (Cimex lectularius) are small, flat insects that primarily feed on human blood. Measuring about the size of an apple seed, these pests often go undetected until they have made a significant presence known through their bites. Historically, bed bugs were a common household pest in many parts of the world, only to diminish in numbers with the advent of insecticides in the mid-20th century. However, recent years have seen a resurgence, and they now pose a considerable threat.
The body structure of bed bugs allows them to find refuge in tight spaces, often lurking in mattresses, box springs, and headboards. This habit makes them challenging to eradicate without a dedicated effort. Moreover, their ability to be dormant for extended periods can help them survive adverse conditions, further aggravating their management in domestic settings.
Historical Context


Historically, bed bugs have been a part of human habitats for thousands of years. They were mentioned in ancient texts, including writings from the Roman Empire and Sanskrit texts from India. Once, they were commonplace in households across Europe and the Americas, thriving in the warm, dark corners of homes.
However, their prevalence dwindled with advances in sanitation and the introduction of pesticides like DDT in the mid-20th century. As urbanization grew, many believed bed bugs had been relegated to history. Yet, since the late 1990s, they have made a notable comeback, attributed to factors such as increased international travel and pesticide resistance. With people moving around more than ever, these pests have had the opportunity to hitch a ride in suitcases, clothing, and even used furniture, re-establishing themselves in places where they were once eradicated.
This rich history underscores the need for ongoing vigilance and informed strategies for management and prevention. Anyone looking to safeguard their home must appreciate not only what bed bugs are but also how they came to be a persistent companion in the human experience.
The Biology of Bed Bugs
Understanding the biology of bed bugs is crucial in grasping how these pests survive and thrive in various environments. Through their unique physical traits and reproductive methods, bed bugs have developed a formidable adaptability, making eradication a complex challenge for homeowners and pest control professionals alike. Knowing the biology of these bothersome insects is like having a key to a lock; it unlocks the mystery of their resilience and provides insight into effective management strategies.
Physical Characteristics
Bed bugs, scientifically known as Cimex lectularius, are small, wingless insects capable of a significant amount of survival due to their unique physical characteristics. Typically, adult bed bugs measure around 4 to 5 millimeters in length, resembling tiny apple seeds. Their color varies from reddish-brown to a darker shade, depending on their feeding status. This small size allows them to easily slip into tight spaces, making detection particularly difficult.
One fascinating aspect of their anatomy is their specialized mouthparts, designed for piercing skin and sucking blood. With elongated beaks, bed bugs can feed for up to 10 minutes, injecting saliva that numbs the bite area and prevents blood clotting, allowing them to thrive without alarmed hosts. Their flexible bodies enable them to swell significantly when filled with blood, which acts as a food reservoir that fuels their survival for weeks without feeding.
Their observations help to highlight how these pests often go unnoticed until the point where an infestation is already established. This characteristic sets the stage for a deeper understanding of % common avenues of introduction into homes, whether through travel or second-hand furniture.
Reproductive Strategies
The reproductive strategies of bed bugs also play a significant role in their survival. A female bed bug can lay anywhere from 200 to 500 eggs during her lifetime, which is roughly 6 to 12 months. These eggs, about the size of a pinhead, are laid in clusters and can easily go unnoticed. Once hatched, nymphs undergo five molts before reaching maturity, which can happen in as little as one month under optimal conditions.
Bed bugs have a rather notorious mating ritual known as "traumatic insemination," where the male bed bug pierces the female's abdomen with his reproductive organ, depositing sperm directly into her body cavity. This controversial method maximizes the chances of successfully fertilizing the female while ensuring high reproductive rates. In essence, it’s a survival tactic that leads to rapid population growth, especially in an environment rich in food sources such as human dwellings.
"Understanding the reproductive cycles of bed bugs is critical to developing effective control measures. Ignoring this aspect can spell doom for any extermination attempts, as new generations can quickly repopulate an infested area."
These biological traits, while seemingly simple, showcase the bed bug's sophisticated nature and adaptability. This adaptability is what makes prevention and eradication efforts so vital; it’s essential to target both adult bugs and their eggs to interrupt their life cycle and protect one’s home effectively. By recognizing the biology behind these pests, homeowners can equip themselves with the knowledge needed to safeguard their living spaces.
For further information, resources such as CDC's Bed Bug page and University of Nebraska-Lincoln's guide offer more insights into effective control methods and biological understanding.
Nutritional Needs of Bed Bugs
Understanding the nutritional requirements of bed bugs is key to grasping their survival strategies. These pests rely on a rather specific diet, primarily consisting of blood, which allows them to thrive in various environments. This section delves into their primary sources of nutrition and the intricacies of their blood feeding mechanisms, providing insights into how these factors contribute to their resilience.
Primary Source of Nutrition
Bed bugs are notorious for their diet, with human blood being their preferred choice. While they can consume blood from other mammals like dogs or cats, it's primarily the warmth and carbon dioxide emitted by humans that attract them. A single feeding session can provide enough sustenance to keep them going for several days, making their dependency on blood quite strategic.
Their feeding typically occurs during the night when people are asleep, taking advantage of their hosts being unaware. This nocturnal feeding pattern not only enhances their chances of survival but also minimizes detection by humans.
"A bed bug can consume about 6 milliliters of blood in one feeding, which is approximately 7 times their own body weight!"
Here's what is particularly interesting about their primary source of nutrition:
- Hemoglobin Utilization: Bed bugs possess specialized enzymes that allow them to break down the hemoglobin in blood efficiently.
- Fermentation: Interestingly, they can also ferment certain components of blood, which aids in their digestion process. This capacity allows them to maximize the nutrients extracted from each feeding session.
- Adaptable Diet: Although they favor human blood, bed bugs can go without food for extended periods. Reports suggest they can live for up to a year without a meal under favorable conditions.
Blood Feeding Mechanism
The blood feeding mechanism of bed bugs is a marvel of nature. Using a specially adapted mouthpart called a stylet, they pierce the skin and access a blood vessel. Here's a closer look at how this process unfolds:
- Detection: The bed bug senses warmth and carbon dioxide, guiding it to its target.
- Preparation: Once they land on the skin, they use their stylet to make a small puncture.
- Saliva Injection: To facilitate feeding, bed bugs inject saliva that contains anticoagulants, preventing the blood from clotting.
- Feeding: After the initial puncture, the bug draws blood through its stylet, effectively draining it.
- Withdrawal: Once satiated, the bug retracts its mouthpart and makes a swift retreat, leaving very little trace behind.
This remarkable feeding mechanism not only illustrates their efficient adaptation but also speaks volumes about how they've thrived alongside humans. The maintenance of a steady food supply through host interactions allows bed bugs to sustain their populations even in changing environments.
The nutritional requirements of bed bugs are not just about survival; they are deeply intertwined with their life cycles and behavioral patterns. As homeowners become more aware of these nutritional needs, they can better understand how to implement effective pest control strategies.
Alternative Survival Strategies
Understanding the various survival strategies of bed bugs is vital when delving into how these resilient pests manage to thrive even amidst efforts to eradicate them. This section highlights the specific tactics that bed bugs employ not only to survive but also to multiply efficiently. Knowing these methods can empower homeowners to adopt more effective prevention and treatment strategies against these unwanted guests.
Starvation Tactics
Bed bugs are notorious for their ability to withstand significant periods without a meal. Their starvation tactics are a fascinating aspect of their survival. When food—namely, human blood—is scarce, bed bugs can simply hunker down, essentially pressing pause on their life processes. Studies show that they can survive for months without feeding, a stark reminder of their resilience.


- Metabolic Adjustment: During periods of starvation, bed bugs reduce their metabolic rate considerably. With a slower metabolism, they conserve energy and resources, allowing them to endure in a dormant state for extended periods.
- Survival Beyond Blood: While they are primarily blood feeders, bed bugs can also subsist on materials like organic debris or even on skin cells that slough off from humans. This adaptive behavior allows them to persist longer in environments where they might not have regular access to blood.
- Effective Environment Utilization: Bed bugs often hide in cracks and crevices, seeking out places with little disturbance, which increases their chance of remaining undetected for longer periods. This selective behavior ensures they can stay hidden until a potential host becomes available.
This remarkable capacity to outlast food scarcity directly influences both their reproduction rates and infestation potential, making it essential for homeowners to be proactive about monitoring and maintaining cleanliness.
Hibernation and Dormancy
In addition to their starvation tactics, bed bugs also employ hibernation forms, taking dormancy to the next level. Depending on the environmental conditions, like temperature and availability of hosts, bed bugs can transition in and out of dormancy, which is a crucial survival strategy.
- Seasonal Adaptations: When temperatures dip, particularly during winter months, bed bugs go into a state akin to hibernation. This transition signifies a decrease in reproduction and activity, helping them conserve energy until conditions become favorable again. They prefer temperatures around 70°F but can survive extreme highs and lows by entering dormancy.
- Pupation Stages: In their life cycle, bed bugs can enter a pupation stage where they become less active and more resilient to environmental stressors. These moments of dormancy can last weeks, giving them time to weather unsuitable conditions until they can emerge in search of food.
- Reactivation Triggers: Changes in their environment, such as increased temperatures or the presence of carbon dioxide from a nearby host, act as signals for bed bugs to reawaken from dormancy. This remarkable ability to adapt and react sharply enhances their resilience and competitiveness against eradication attempts.
"Bed bugs can survive for months without feeding, making them one of the most enduring pests to tackle in any home."
Environmental Adaptations
In the intricate world of bed bugs, environmental adaptations play a crucial role in their survival and proliferation. These adaptations are not merely survival tactics; they represent a complex interplay between the bed bugs and their habitats, demonstrating resilience in the face of changing conditions. Understanding how bed bugs have evolved to thrive in human environments can provide valuable insights for homeowners and pest management professionals alike.
Effective environmental adaptations allow bed bugs to exploit various niches where food and refuge are available. With many homes being filled with nooks and crannies, bed bugs find themselves in an ideal breeding ground. These highly adaptable pests can withstand a range of environmental conditions, ensuring they can persist even in less-than-ideal surroundings. Key aspects include temperature tolerance and the selection of hiding places that not only offer safety but also proximity to their primary source of sustenance – human blood.
One significant benefit of understanding these adaptations is the ability to implement more targeted preventative measures. By identifying and altering the conditions that favor bed bug survival, homeowners can create an unwelcoming environment for these pests. For instance, the maintenance of lower temperatures or a reduction of clutter can hinder their ability to find suitable hiding spots, thus lowering the likelihood of infestation.
Temperature Tolerance
Bed bugs exhibit a remarkable capacity for temperature tolerance, which is integral to their survival. They can endure a surprisingly wide range of temperatures, from below freezing to over 120 degrees Fahrenheit. Their ability to adapt to varying temperatures allows them to reside comfortably in diverse climates and settings without much fuss.
Interestingly, bed bugs have a crucial threshold. While they can survive at extremely low temperatures for short periods, prolonged exposure can be lethal. Similarly, high temperatures can kill bed bugs, but only if maintained consistently over time. For instance, techniques like heat treatment can effectively eradicate these pests when temperatures exceed 120 degrees Fahrenheit for over an hour. Homeowners should recognize this vulnerability and consider temperature manipulation as part of their pest control strategies.
Habitats and Hiding Places
When it comes to finding shelters, bed bugs have quite the knack for ingenuity, being particularly fond of dark, secluded spots where they can hide undetected. They are drawn to areas close to where humans rest or sleep, making beds, furniture, and even baseboards prime real estate for their nests.
Some common hiding spots include:
- Mattresses and Box Springs: These are often the first places where bed bugs set up shop. The seams and folds offer both comfort and accessibility to blood meals.
- Cracks and Crevices: From behind wallpaper to within the wooden frameworks of furniture, these tiny spaces provide excellent cover.
- Luggage and Personal Items: Bed bugs can easily hitch a ride in luggage, especially when travelers stay in infested accommodations.
"Understanding the favorite hiding spots of bed bugs enables homeowners to act preemptively, minimizing the risk of infestation and aiding in prompt eradication should it occur."
By being aware of these habitats, homeowners can develop preventative measures, such as regular inspections of these high-risk areas. Keeping a clean, organized living space can also help mitigate the likelihood of inviting these unwelcome guests.
Overall, the adaptations of bed bugs are a testament to their resilience, proving challenging to manage. However, a firm understanding of their preferred temperatures and hiding spots can aid homeowners in devising effective countermeasures, potentially reducing the chances of a severe infestation in their living spaces.
Impact of Human Activity
The role human behavior and urban development play in the survival and dissemination of bed bugs cannot be overstated. These small, pesky vampires thrive on the chaos of modern society, finding new ways to hitch rides and proliferate in various environments. Effectively understanding this impact provides crucial insights into prevention and control strategies, especially for homeowners and pest management professionals. The intersections of urbanization, travel, and people's day-to-day choices create a perfect storm for bed bug infestations.
Urbanization and Infestation
As cities expand, the density of living spaces increases, inadvertently creating ideal conditions for bed bug infestations. In densely populated metropolitan areas, numerous factors contribute to the ease with which these bed bugs spread:
- Close Proximity of Housing: In cities with apartment buildings or shared common spaces, bed bugs can easily migrate from one unit to another. Just imagine a neighbor unknowingly bringing these bugs home from a recent trip—it can spark an infestation that spreads rapidly through the building.
- High Turnover Rates in Rentals: Urban centers often see a high turnover of tenants, and each new occupant might unintentionally introduce bed bugs into their new homes. What’s worse, some people are unaware they are bringing along unwanted house guests, leading to silent infestations.
- Frequent Use of Public Transport: Commuters can unwittingly transport bed bugs from one location to another, making buses, trains, and taxis prime targets for these pests. Just a single ride can lead to their settlement in new areas.
- Increased Mobility: The fast-paced lifestyle that many lead in the city often results in people traveling regularly, visiting hotels, or staying in temporary accommodations. Unfortunately, these places can often be breeding grounds for bed bugs, which latch on to luggage, clothing, and other personal belongings for a free ride.
Humble Fact:
"A single female bed bug can lay up to five eggs a day, leading to thousands of potential offspring within a few months if not effectively managed." This reality throws a spotlight on the urgent need for awareness and proactive measures in urban environments.
Global Travel Patterns
The interconnectedness brought about by globalization presents further challenges in the fight against bed bugs. Travel has never been more accessible, leading to increased cross-border movement of both humans and pests. Consider the implications of this increased mobility:
- International Travel: Tourists visiting from various countries can unknowingly carry bed bugs into their cities, facilitating the spread of occurrences from one region to another, sometimes even continents.
- Airports and Hotels: These are prime hotspots for infestations. With billions of travelers passing through each year, bed bugs can easily hitch a ride in luggage or on clothing. The moment a person checks into a hotel room, they might unwittingly bring along these pests, starting a new cycle of infestation.
- Online Commerce: With the popularity of online shopping, purchasing second-hand items or even new ones becomes a risky business. An unsuspecting buyer might bring home bed bugs hiding in that vintage suitcase or refurbished furniture.
In summary, as human activity becomes more intertwined with the lifestyles we lead and the environments we inhabit, awareness and proactive steps become vital in curbing bed bug populations. Whether through maintaining cleanliness, elevating vigilance during travel, or implementing effective prevention strategies, understanding the effects of urbanization and global travel is essential in the battle against these resilient pests.
Eradication Challenges


Addressing the eradication of bed bugs is no simple feat. Their increasing presence in homes poses significant challenges. As homeowners, understanding these challenges is crucial for effective pest management. It’s not just about squashing a few bugs. We need to consider several factors that make bed bugs a persistent nuisance.
First, resistance to insecticides has become a major hurdle in controlling bed bug populations. The bugs are tougher than they appear; many are developing a certain invulnerability to over-the-counter treatments. This resistance is significant. It raises questions about the usual methods employed to deal with them.
Moreover, the effectiveness of common treatments is often less than stellar. Homeowners can find themselves flinging money at sprays and traps that hardly make a dent in their bed bug issues. It often feels like a never-ending game of whack-a-mole, where each time one bug is exterminated, another seems to pop up. This unpredictability tends to leave many folks feeling overwhelmed and frustrated.
With these points in mind, it’s crucial to explore the deeper roots of these eradication challenges. A lack of awareness about bed bug behavior can significantly impede timely interventions. Homeowners must prioritize education about these pests to make informed decisions about methods and products used in extermination efforts.
"Understanding the bugs’ strategies provides you with the upper hand in the battle against their invasion."
To tackle these issues effectively, employing integrated pest management strategies is often recommended. This could involve a combination of chemical treatments and non-chemical interventions tailored to the specific infestation. Now, the question arises: How can we arm ourselves with information to improve our chances of successful eradication?
Prevention Strategies
Preventing bed bugs from infesting your home is as crucial as understanding their survival strategies. This part of the discourse will highlight practical steps and considerations that can help homeowners safeguard their living spaces. Proactive strategies are not just about reacting to an infestation, but rather about creating an environment that discourages these pests from making a home in your bedding and furniture.
Home Maintenance Techniques
Keeping your home in tip-top shape plays a vital role in prevention. If you want to keep these uninvited guests at bay, you might want to start by regularly inspecting your living quarters. Here are a few suggestions:
- Regular Cleaning: Frequent vacuuming of carpets, floor spaces, and upholstery can go a long way. Not just any clean, but a thorough vacuum that gets into the nooks and crannies, where these pesky bugs love to hide. Focus on areas like bed frames, headboards, and behind furniture.
- Decluttering: A clutter-free home is a happy home - for humans and pests alike. Reducing clutter minimizes the places where bed bugs can hide and makes it easier to identify and treat an infestation if it occurs. Be mindful of the items you place in storage; those old boxes may have more than just memories.
- Sealing Cracks and Crevices: Inspect your home for any cracks or crevices that could serve as entrances for bed bugs. Sealing these openings with caulk or other appropriate materials can serve as a barrier to them.
- Protective Covers: Consider using mattress and pillow encasements that are specifically designed to prevent bed bugs. These covers can help keep any lurking bugs contained and make cleaning and inspection much easier.
"An ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure." - Benjamin Franklin
Awareness and Education
Education is a powerful tool in the fight against bed bugs. With the right knowledge, homeowners can better recognize the signs of infestation early on and respond promptly. Here are some practical areas to focus on:
- Identifying Signs of Infestation: Bed bugs can often go unnoticed until it’s too late, so understanding their signs is crucial. Familiarize yourself with signs like dark spots on bedding (their excrement), small blood stains, or even the bugs themselves, which are often walnut-sized and reddish-brown in color.
- Understanding Bed Bug Habitats: Knowing where bed bugs like to hang out—bed frames, mattresses, and even behind picture frames—can help you stay vigilant in your inspections. Make it a habit to check these hotspots regularly, especially after guests leave or when traveling.
- Resources for Education: Tap into online resources for valuable information and updates. Websites like CDC and EPA often provide the latest information about bed bug prevention and treatment. Joining local community forums or discussion groups on sites like Reddit can also help you learn from others' experiences.
In summary, safeguarding your home against bed bugs hinges on a two-fold approach: diligent home maintenance and continuous education. Prevention demands consistent effort and attention, yet the peace of mind that comes with it is well worth the endeavor.
Ending
In summarizing the intricate relationship between bed bugs and their survival mechanisms, this discussion emphasizes how crucial it is for homeowners to understand these pests. Knowledge of their behaviors, nutritional habits, and environmental adaptations not only aids in effective prevention strategies but also informs extermination efforts. It helps to demystify the challenges of bed bug infestations, which are often misunderstood and dismissed.
The complexity of bed bug resilience against eradication methods underscores the importance of employing multi-faceted approaches in combating these pests. Homeowners must treat their living spaces as prime real estate for these critters, making thorough inspections and maintaining cleanliness paramount. Being aware of their hiding spots and understanding their feeding habits adds layers to any prevention strategy. Regular inspections and using encasements can prevent a small problem from blossoming into a full-blown invasion.
"A stitch in time saves nine" — this adage is fitting when it comes to addressing bed bugs. Tackling infestations early is not just about comfort; it is also about health, budget management, and maintaining a peaceful home environment.
Additionally, human behavior and urbanization play a significant role in bed bug proliferation. Pictures of the incessant travel and increasing shared living spaces paint a broader picture of their resurgence. Thus, education and awareness among the public and individuals in pest management efforts are essential.
Summarizing Key Points
In this article, we have covered the following key points regarding bed bugs:
- Biology and Behavior: Understanding their biological makeup, reproductive tactics, and feeding mechanisms provides insight into their resilience.
- Survival Strategies: Their ability to withstand starvation and go dormant during unfavorable conditions showcases their adaptability.
- Environmental Factors: Analyzing how temperature and different habitats affect their lifestyle reinforces why they are difficult to eliminate.
- Human Interactions: We’ve explored how urbanization and global travel patterns have inadvertently facilitated their spread, making awareness crucial.
- Preventive Measures: The focus was on practical home maintenance techniques and the need for education in preventing infestations.
Future Directions in Research
Looking ahead, future research into bed bugs could significantly enhance our understanding and management of these pests:
- Genetic Studies: Exploring the genetic resilience of bed bugs may lead to new tactics for pest control by targeting their adaptations at a molecular level.
- Behavioral Research: A deeper investigation into the behavioral tendencies of bed bugs can lead to innovative preventative methods that exploit their habits.
- Eco-Friendly Eradication Methods: Research into non-toxic, environmentally friendly methods of extermination can help in managing infestations effectively without harming human health.
- Impact of Climate Change: Understanding how changing climates affect bed bug populations around the world could inform where infestations are likely to arise next.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Initiatives focused on educating residents about prevention and early detection systems could foster better communal management of these pests.
Each of these areas not just advances our scientific knowledge but also supports homeowners in making informed decisions on how to protect their living spaces, ensuring peace of mind in their homes.
Benefits of Including References
- Credibility: When you cite reputable sources such as academic journals, government reports, or expert studies, it enhances the trustworthiness of your arguments. This is vital for homeowners and pest control professionals striving to make informed decisions.
- Contextual Understanding: References allow readers to dive deeper into specific aspects that may not be fully covered in the article. For instance, if a reader wishes to understand more about insecticide resistance, they can refer to studies laid out within the references.
- Encouragement of Further Research: Providing citations encourages readers to explore related topics, fostering a richer understanding of pest-related issues beyond the immediate scope of this article.
Specific Considerations
- Diversity of Sources: It's vital not just to reference popular articles, but also include lesser-known studies or reports that contribute a unique perspective. Scholarly articles often reveal insights not available in mainstream publications.
- Recency Matters: Given how rapidly our understanding of pests evolves, including the latest research can provide readers with current practices and strategies. Information from the past may not always hold true today, especially with advancements in pest control methods.
- Dissemination of Knowledge: Linking to online forums, educational websites, or community resources allows readers to engage with the topic interactively. Websites like Wikipedia, Britannica, or even Reddit have valuable information and discussions around bed bugs that can aid in ongoing learning.
"An informed homeowner is the first line of defense against bed bug infestations."
- Examples of Useful References:
- Government resources (.gov) regarding pest control metrics and statistics.
- Educational websites (.edu) that provide insight into entomological studies.
- Peer-reviewed journals that give detailed insights into bed bug biology and behavior.
In summary, the references section is more than just a list; it’s a gateway to further knowledge. By emphasizing research and reputable sources, you lay a foundation for understanding that benefits not only the article but also empowers readers in their battle against bed bugs.



