Understanding Chiggers: Identification and Symptoms


Intro
Chiggers are tiny, bustling mites that can cause significant discomfort when they invade our personal space. Understanding these pests begins with correct identification and recognizing symptoms associated with their bites. In this article, we will explore the defining characteristics of chiggers, symptoms related to their presence, and effective prevention and management techniques. By equipping ourselves with knowledge, we can tackle the issues stemming from chigger infestations, ensuring both personal comfort and the health of our environments.
Understanding Pests
Definition of Pests
Pests generally refer to organisms that adversely affect human activities, whether in agriculture, home environments, or public health. Chiggers fall under this category, being the larval stage of red mites. These parasites primarily seek out human hosts for feeding and are often found in grassy or wooded areas, where they thrive in warm, damp climates.
Importance of Pest Identification
Accurate pest identification is crucial for effective management. Misidentifying a pest can complicate control measures and lead to ineffective solutions. Knowing whether the itching on your skin is caused by a chigger bite, mosquito bite, or other insects can shape one's response. Chiggers can lead to intense itching and irritation. Understanding their lifecycle and behavior can guide us in developing appropriate strategies for prevention and treatment.
Prevention Techniques
Home and Garden Preventative Measures
Preventing an infestation begins at home and in our gardens. Here are some practical measures:
- Maintain a Well-Groomed Yard: Regularly mow the lawn and trim overgrown shrubs. This reduces the areas where chiggers can reside.
- Install a Barrier: Gravel or wood chip borders around gardens can create a natural barrier against chiggers.
- Use Appropriate Ground Cover: Dense grass or weeds are ideal habitats for chiggers. Opting for mulch or other non-grassy ground coverings can minimize their presence.
Seasonal Prevention Tips
Understanding the seasonal patterns of chigger outbreaks can aid in preventing infestations:
- Spring Care: Chiggers become particularly active in the spring when temperatures rise. Ensuring your garden is tidy during this time can help eliminate potential breeding sites.
- Summer Precautions: Using repellents containing DEET before outdoor activities can lower the likelihood of bites during summer excursions.
Eco-Friendly Pest Control Solutions
Overview of Sustainable Practices
When dealing with chigger infestations, eco-friendly control solutions are desirable for both environmental integrity and safety. These solutions often prioritize preventative measures and reduce the reliance on harsh chemicals. Utilizing organic pest deterrents can keep your home and garden healthy, while also removing the chances of chigger invasions.
Natural Remedies and Their Effectiveness
Several natural remedies can help alleviate chigger bites and prevent future issues:
- Essential Oils: Oils like eucalyptus and tea tree oil can act as natural repellents. Diluting them with a carrier oil and applying to the skin can provide some relief.
- Vinegar and Baking Soda Pastes: Applying paste made from vinegar and baking soda can soothe the itching and reduce irritation from bites.
"Creating awareness about chiggers helps readers make informed decisions regarding pest control and personal health."
In examining chiggers, one recognizes their potential for discomfort and the importance of understanding their presence in our environment. Conclusively, effective pest management integrates identification, prevention, and remedial actions.
Preamble to Chiggers
Chiggers often escape notice, yet they influence outdoor experiences and wellness. Understanding chiggers is essential, especially for those who spend time in nature. This knowledge helps identify infestations, design effeective prevention strategies, and mitigate consequences of bites.
Their small size belies a significant impact. Many may not know the steps to identify chiggers even when they see them. Recognizing their presence means that a person can take required actions to avoid bites. This is crucial, as chigger bites lead to discomfort and potential skin issues.
Awareness empowers readers to keep homes and yards safe. Emphasizing preventive measures reduces risk of encounters with these parasites. Furthermore, knowing their lifecycle aids in understanding how and why chiggers thrive in certain conditions.
In summary, establishing a solid foundation regarding chiggers gives insight into pest management. This portion of the article lays groundwork for deeper dives into specific aspects of chiggers.
What Are Chiggers?
Chiggers are larvae of certain species of mites, commonly found in grassy and wooded areas. These microscopic parasites thrive in various habitats, primarily feeding on warm-blooded animals, including humans. Unlike ticks, chiggers do not drink blood. They inject saliva that digests skin cells, leading to irritation and the characteristic itching associated with their bites.
Lifecycle of Chiggers
Understanding the lifecycle of chiggers provides clarity on their habits and helps in managing them.
Egg Stage
The egg stage marks the beginning of a chigger's life. Eggs are laid in clusters on soil or vegetation. They generally hatch within a few days, contributing to rapid population growth. The tiny larvae emerge ready to seek hosts for feeding. This stage emphasizes the potential for large infestations in an area.
Lavral Stage
During the larval stage, chiggers are particularly active in seeking out a host. The larvae have six legs and appear red or orange. Their primary survival tactic involves attaching to a host to feed. This is critical as it ensures the continuation of their lifecycle. Implementing preventive measures at this stage can significantly reduce the chances of bites.
Nymph Stage
After feeding, chiggers molt into nymphs. In this stage, they develop additional legs, gaining eight like adult mites. Nymphs do not feed on humans; instead, they rely on smaller hosts, which may include insects. This stage is less of a concern for human health but is vital for understanding the overall lifecycle.
Adult Stage
Finally, chiggers reach adulthood. Adults primarily feed on smaller animals and do not pose the same risk to humans as their juvenile counterparts. Nonetheless, it's essential to note their role in the ecosystem. Adults contribute to controlling insect populations. Understanding the adult stage emphasizes the need for specific control measures during the larval phase when they are most problematic to human health.
Habitat and Behavior
Understanding the habitat and behavior of chiggers is crucial in recognizing their presence and mitigating encounters. These factors influence the environments where chiggers thrive, their life cycles, and potential interactions with humans. Knowing where chiggers are likely to inhabit can greatly assist individuals in taking preventive measures against bites and infestations.
Where Do Chiggers Live?
Natural Habitats
Natural habitats are fundamental to the life of chiggers. They typically reside in environments that provide moisture, dense vegetation, and various host animals. Such environments include forests, grasslands, and wetlands. These factors contribute significantly to their survival and reproduction.
A key characteristic of natural habitats is the availability of organic matter, which supports a diverse ecosystem. These areas are often rich in biodiversity, offering chiggers a broad range of potential hosts. An advantage of chiggers dwelling in natural settings is the abundance of food sources, allowing their populations to flourish. However, these locations can also mean an increased risk of exposure for individuals who venture in these areas.
- Advantages: Rich in hosts and microbiomes beneficial for their survival.
- Disadvantages: High exposure risk for humans, particularly during outdoor activities.
Urban Environments
Urban environments present a contrasting habitat for chiggers. Despite the concrete landscape, they can be found in gardens, parks, or any area with soil and grass. These settings often provide shelter and are frequented by humans and pets.
The key characteristic of urban environments is modified ecosystems. They often lack the diverse flora that natural areas provide but can still harbor chiggers due to the presence of host animals, such as cats and dogs. A unique feature of urban habitats is their proximity to human populations. This closeness can lead to greater human-chigger interactions, increasing the chances of bites and infestations.
- Advantages: Easier for people to recognize potential infestations and address them more rapidly.
- Disadvantages: Increased risk of contact due to urban dwellers not being fully aware of chigger presence in populated areas.
Feeding Habits
Chigger feeding habits are integral to their survival and the symptoms observed in humans following bites. Their specific preferences and techniques contribute to understanding potential risks associated with them.
Host Selection
The process of host selection is vital for chiggers. They seek out warm-blooded animals, as these species provide the necessary nourishment for larvae. Mice and other small mammals are common hosts due to their prevalence in various environments.
A crucial characteristic of host selection is the occurrence of host-finding behaviors. Chiggers can detect hosts through sensory cues, which enables them to effectively locate suitable feeding sites. This behavior is beneficial for chigger survival, but also problematic for humans, leading to bites during outdoor activities.
- Advantages: High success rate at finding appropriate hosts ensures chigger survival.
- Disadvantages: Increased incidents of bites when humans unknowingly enter these habitats.
Feeding Mechanism
Chigger feeding mechanisms are distinct and crucial to understand when discussing their impact on humans. Chiggers do not fully ingest their hosts; instead, they inject saliva into the skin to digest tissues, leaving behind intense itching and irritation.
A key characteristic of this feeding mechanism is its efficiency. The saliva contains enzymes that break down epidermal cells, allowing the chiggers to feed without the need for prolonged attachment to the host. As a result, this process leads to the characteristic red bumps and swelling associated with chigger bites.
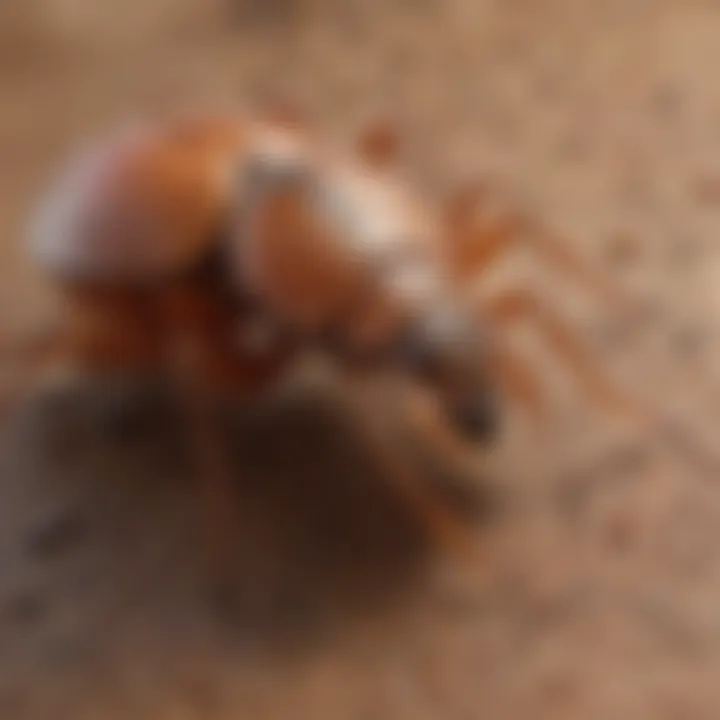


- Advantages: Effective method of nutrient extraction increasing survival rates.
- Disadvantages: Causes severe discomfort for the host, leading to irritation.
In summary, understanding chiggers' habitats and feeding habits provides necessary insight into their life cycle and behavior. Recognizing these factors can help individuals minimize encounters, thereby reducing the risk of bites and their associated symptoms.
Identifying Chigger Bites
Identifying chigger bites is a crucial part of understanding these parasites. Knowledge of symptoms helps individuals determine the presence of these pests and can guide effective management strategies. Early recognition of bites allows for prompt treatment, thereby reducing discomfort and the risk of secondary infections. By being aware of the signs, homeowners can take proactive measures to prevent further exposure to chiggers.
Symptoms of Chigger Bites
Itching
Itching is the most common and immediate symptom associated with chigger bites. This sensation typically begins a few hours after the bite occurs. Itching can range from mild to severe, often resulting in intense discomfort. This key characteristic makes itching a notable sign in recognizing chigger bites.
The unique feature of itching from chigger bites stems from the enzymes they inject into the skin while feeding. This enzymatic reaction causes inflammation and irritation, leading to the itching sensation. While this itch is unpleasant, it serves as a reminder for individuals to investigate potential bites, facilitating timely treatment efforts.
Red Bumps
Red bumps often develop at the site of chigger bites, contributing significantly to the overall recognition of these pests. They can be small and relatively isolated or may form clusters, depending on the extent of bites in a particular area. The appearance of red bumps is a characteristic reaction to chigger mocrowounds and alerts affected individuals to the possibility of an infestation.
The unique feature of these red bumps is their formation as a response to the body’s histamine release. While these bumps can be unsightly and may incite further itching if scratched, they are generally harmless. Recognizing these signs can inspire preventive steps to limit chigger exposure and avoid further biting.
Swelling
Swelling around the bite site is another common symptom that individuals may experience after a chigger bite. This occurs due to localized inflammation as the body's immune system responds to the enzymes introduced by the chigger. The key characteristic of swelling is that it can amplify the feeling of discomfort caused by the bites.
Swelling can vary in intensity from mild to pronounced, often causing concern among those affected. The unique feature of swelling is that it indicates a more intense allergic response, which may necessitate targeted treatment. Notably, excessive swelling may impede movement, signifying the need for appropriate care to alleviate symptoms.
Differentiating from Other Bug Bites
Differentiating chigger bites from those of other insects, such as mosquitoes, ticks, and fleas, is critical for effective management. Understanding the nuances in bites allows individuals to recognize when they are dealing specifically with chigger issues, leading to better prevention tactics.
Mosquito Bites
Mosquito bites are typically characterized by small, raised welts that are often quite itchy. Unlike chigger bites, mosquito bites can occur quickly and are usually associated with outdoor exposure during the evening. Recognizing these bites is beneficial as they can indicate different types of pest control needs, especially in moist environments.
Moreover, mosquito bites can transmit diseases, making it imperative to avoid further exposure. Individuals should be aware that both mosquito and chigger bites may elicit itching, but the timing and environment of the bites may differ greatly.
Tick Bites
Tick bites often appear as small red spots, similar to chigger bites, but they have a critical distinguishing factor: tick bites may lead to more serious health risks, such as Lyme disease. Ticks tend to remain attached to the skin longer than chiggers, making it essential to inspect for tick presence after spending time in wooded areas.
Understanding the difference is crucial, as improper management of tick bites could lead to health problems that chiggers do not present. Awareness of these differences ensures that individuals pay attention to possible tick-related complications, necessitating medical consultation.
Flea Bites
Flea bites are usually found on the lower legs and are also quite itchy. They may present as red spots with a distinct pattern, often grouped together, which can be another indicator of infestation. Recognizing flea bites can help homeowners address potential pest control issues, particularly if pets are involved.
The unique feature of flea bites is their association with pets and bedding. Understanding this relationship can aid in establishing cleanliness routines that minimize further exposures to chiggers or other pests.
It's essential to recognize the characteristics of chigger bites and how they differ from other bug bites to take appropriate action and maintain a healthy living environment.
Diagnosis of Chigger Infestation
Diagnosing a chigger infestation is crucial for understanding how to combat these pests. It helps in confirming whether the symptoms present are indeed due to chigger bites or caused by other factors. Early diagnosis can lead to prompt management, reducing discomfort and preventing complications.
Effective diagnosis involves recognizing specific signs, as well as understanding when to seek medical advice. This proactive approach not only alleviates anxiety but also informs personal treatment options.


Signs of Infestation
Observable Skin Reactions
Observable skin reactions are often the first sign of chigger bites. These reactions typically manifest as intense itching and red bumps on the skin. The itching results from a chemical found in the chigger's saliva that reacts with the skin. This characteristic is instrumental in isolating chigger infestations, as it is distinctly different from reactions caused by other insect bites.
One unique feature of these skin reactions is the presence of clustered bite areas, commonly found around the waist, ankles, or where clothing fits tight.
Benefits of recognizing these observable reactions include the ability to take early preventive measures and reducing the risk of secondary infections due to scratching. However, it can also lead to confusion with other common insect bites, thus requiring careful observation.
Location of Bites
Location of bites provides insight into identifying chigger infestations. Chigger bites typically occur in specific areas of the body where the skin is thinner or where there is tight clothing. These bites often appear in clusters, which is a key characteristic that distinguishes them from bites from mosquitoes or fleas.
This specific location feature is beneficial, as it narrows down the potential culprits when determining the cause of skin irritation. People often notice bites on areas such as the legs, arms, and torso. The clustered pattern can help homeowners and housewives to quickly assess and respond to a potential infestation.
Recognition of bite locations can aid in early diagnosis. However, individuals may misinterpret these signs, thinking they are caused by other pests. Given the similarities in bite locations with other insects, careful inspection is essential.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Individuals should consider seeking medical attention if they experience severe symptoms, such as excessive swelling, signs of infection like pus, or if the itching is unmanageable. These symptoms may indicate that a simple chigger bite has escalated into a more serious issue that requires professional care.
Understanding these signs not only helps in personal health management but also provides insight into effective strategies for prevention and treatment of chigger bites in the future.
"Early diagnosis and proper management can significantly reduce the discomfort associated with chigger bites, leading to a quicker recovery.”
Effective Management Strategies
Effective management strategies form the backbone of dealing with chigger infestations. Understanding how to prevent bites and knowing how to treat them is crucial for both comfort and health. These strategies not only minimize the likelihood of exposure to chiggers but also ensure that when bites occur, their symptoms can be effectively managed. Creating a robust plan that combines prevention with treatment fosters a safer living environment, especially for those with children or pets.
Preventive Measures
Personal Protective Equipment
Personal protective equipment (PPE) plays an essential role in preventing chigger bites. Items such as long sleeves, long pants, and closed-toe shoes create a barrier between skin and these parasites. A key characteristic of PPE is its ability to limit skin exposure. This proactive approach greatly reduces the chance of encountering chiggers in infested areas. In addition, specially treated clothing with insect repellent can offer an extra layer of defense against these pests. The unique feature of PPE lies in its physical barrier, which is straightforward yet significantly effective. However, relying solely on clothing may not be sufficient in heavily infested regions.
Environmental Modifications
Environmental modifications are another crucial aspect of preventing chigger bites. By altering the landscape around home, risks can be minimized. A key characteristic of these modifications includes keeping grass short, removing debris, and creating clear barriers between lawns and wooded areas. These actions make outdoor spaces less inviting to chiggers. One unique feature of environmental changes is that they address the habitat directly, reducing the chances of infestations over time. A potential disadvantage is the ongoing effort required to maintain these modifications, especially in densely vegetated areas.
Treatment Options for Chigger Bites
Over-the-Counter Remedies
Over-the-counter remedies offer immediate relief from chigger bites. Products containing hydrocortisone or antihistamines are often used for reducing itching and inflammation. The key characteristic of OTC remedies is their accessibility. They are widely available and can be applied quickly to alleviate discomfort. Unique to these treatments is their convenience, providing fast relief without waiting for a prescription. However, while effective for mild cases, individuals with severe reactions may find that over-the-counter options do not suffice.
Home Treatments
Home treatments can provide effective relief from chigger bites as well. Simple solutions, such as applying calamine lotion or baking soda paste, can alleviate symptoms quite effectively. The key characteristic of home treatments is their affordability and easy availability of ingredients, which makes them a popular choice among homeowners. A unique feature of these treatments is that they can be prepared quickly with common household items. However, effectiveness can vary widely among individuals, and some may require commercial products for satisfactory relief.
When to Use Prescription Medications
In some situations, prescription medications may become necessary. This is often the case for individuals with severe allergic reactions or those who do not respond well to OTC treatments. The key characteristic of prescription medications is their tailored approach to treating more pronounced symptoms. They can offer stronger antihistamines or corticosteroids if needed. The unique advantage here is that a healthcare provider will create a treatment plan specifically suited to the patient's needs. However, timing is crucial, as delays in seeking prescriptions can lead to unnecessary discomfort.
End
The discussion on chiggers, their identification, and the symptoms associated with their bites holds significant relevance for those who may come into contact with these parasites. Understanding chiggers enables individuals to recognize their presence quickly and take proper actions to manage and prevent further issues. The comprehensive information on identifying chigger bites, differentiating them from other insect bites, and implementing effective management strategies is crucial for maintaining personal health and well-being.
Summary of Identification and Management
Being informed about chiggers aids in swiftly identifying bites, which are characterized by intense itching and red bumps. Individuals should pay attention to the specific areas on the body where bites occur, as these can signal an ongoing infestation. Proper management involves preventive measures, such as wearing protective clothing and utilizing insect repellents in high-risk areas. Treatment options include over-the-counter remedies and home treatments to alleviate symptoms. This knowledge empowers individuals to combat the discomfort caused by chigger bites and seek medical attention if necessary.
Future Considerations in Chigger Research
Looking ahead, research on chiggers presents valuable opportunities to better understand their biology, behavior, and potential impacts on human health. As residential areas expand into natural habitats, the likelihood of chigger encounters may increase. Continued studies addressing their lifecycle, ecological role, and effective management techniques are essential for developing improved methods of control. Understanding how climate change might influence chigger populations can also inform future prevention strategies. Engaging in such research can pave the way for innovative solutions to reduce the incidence and effects of chigger bites in both urban and rural settings.



